In any electrical or data transmission setup, cable insulation plays a crucial role. It serves as a protective layer that not only safeguards the conductors inside but also ensures efficient and safe operation.
Cable insulation separates the conductors from external environmental factors, reducing the risk of electrical leaks, physical damage, and interference with signal transmission.
Selecting the right insulation for your cables isn’t just a technical choice; it’s essential for enhancing the lifespan, safety, and performance of your equipment.
At Cableworld, we understand that the right insulation is vital for both durability and operational safety. We supply a wide range of high-quality cables with insulation materials specifically designed to meet the demands of various applications.
Our aim with this guide is to provide you with the insights you need to make an informed choice on cable insulation.
What is Cable Insulation?
Cable insulation is the protective material surrounding the electrical conductors within a cable. Its main purpose is to shield the conductors from external elements that might interfere with their function, such as moisture, chemicals, and physical impact.
Insulation not only prevents direct contact with other conductive materials but also minimises the risk of short circuits, which can lead to overheating or even electrical fires. By acting as a barrier, cable insulation helps to maintain the performance and reliability of electrical systems.
Role of Cable Insulation in Electrical Systems
In any electrical or data-driven system, insulation is integral to ensuring stable and secure operation. It prevents current leakage by keeping the electric charge contained within the conductors, thereby enhancing efficiency and safety.
Additionally, insulation maintains signal integrity by reducing interference and crosstalk, which is essential for applications that require precise data transmission, such as telecommunications and industrial automation.
Moreover, quality insulation can withstand high temperatures and mechanical stresses, making it ideal for environments where cables face extreme conditions.
By choosing the right insulation, you’re not only optimising the performance of your system but also ensuring compliance with safety standards and regulations.
Key Properties of Cable Insulation
Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength refers to the insulation material's ability to withstand electrical stress without breaking down.
High dielectric strength is crucial for cables used in high-voltage applications, as it ensures the insulation can effectively prevent electricity from escaping the conductor and causing short circuits or dangerous faults.
This property directly impacts the cable’s safety and longevity in environments where strong electrical currents are present.
Thermal Resistance
In many industrial and high-performance applications, cables are exposed to elevated temperatures, which can degrade the insulation over time.
Insulation with high thermal resistance helps maintain cable integrity by preventing heat damage, ensuring that cables continue to perform reliably in high-temperature environments.
This property is essential in settings like factories, power plants, and areas with heavy electrical loads.
Flexibility and Durability
Cables often undergo bending, twisting, and flexing, particularly in applications that require movement, such as robotics, machinery, and mobile equipment.
Insulation that provides both flexibility and durability ensures the cable can withstand physical stress without cracking or deteriorating.
Flexible insulation extends the cable’s lifespan, especially in dynamic installations where consistent movement or bending is common.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Cables in industrial and outdoor environments are frequently exposed to chemicals, moisture, UV rays, and other harsh conditions. Insulation materials that resist these factors are essential for maintaining cable functionality over time.
Chemical and environmental resistance is particularly important in settings such as chemical processing plants, outdoor telecommunications installations, and other applications where cables may be subject to challenging external conditions.
Common Cable Insulation Materials
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
PVC is one of the most widely used insulation materials, prized for its affordability and versatility. It offers moderate flexibility, which makes it suitable for a range of applications, including residential wiring and commercial installations.
PVC also provides some resistance to chemicals and moisture, making it a solid choice for general-purpose cables. It’s especially popular in environments where budget-friendly solutions are needed without extreme environmental demands.
XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene)
Known for its exceptional dielectric strength, XLPE is well-suited for high-voltage applications. This insulation material is resistant to heat and can maintain performance at higher temperatures, making it ideal for heavy-duty environments.
XLPE insulation is common in industrial and power distribution cables, where durability and reliability under electrical stress are essential.
Teflon (PTFE)
Teflon, or PTFE, is a premium insulation material with excellent resistance to extreme temperatures, chemicals, and moisture. This makes it ideal for specialised environments like aerospace, telecommunications, and defence industries, where cables are exposed to harsh conditions.
Teflon insulation is highly durable and remains stable even in temperatures that would damage most other insulation types, making it suitable for critical applications.
Rubber Insulation
Rubber insulation offers outstanding flexibility and resilience, which is beneficial in both indoor and outdoor applications where cables need to move or bend frequently.
Rubber-insulated cables are commonly found in settings like construction sites, industrial machinery, and areas requiring high flexibility. Rubber’s natural durability also makes it effective in protecting cables from minor abrasions and general wear and tear.
Silicone
Silicone insulation is highly valued for its extreme heat resistance and flexibility. This material can endure both high and low temperatures, making it suitable for applications in the medical, food processing, and high-temperature industrial sectors.
Silicone is also biocompatible and safe for applications where human safety is a priority, such as in medical devices or food equipment.
Applications of Cable Insulation
Industrial and Manufacturing Settings
In industrial and manufacturing environments, cables are frequently exposed to high stress, elevated temperatures, and potentially hazardous chemicals. Durable and resistant insulation is critical to protect these cables from damage and degradation, ensuring they can handle the demands of machinery, automation, and power distribution.
Insulation in these settings also serves to prevent electrical faults and potential accidents, making it essential for maintaining safe and efficient operations.
Residential and Commercial Buildings
In homes and commercial buildings, the right insulation type is essential for general wiring, lighting, and power applications. PVC is often used here due to its affordability and sufficient durability for indoor conditions.
Insulation in these settings must provide reliable protection from daily wear while keeping occupants safe from electrical hazards. Cable insulation in these buildings also supports energy efficiency and reduces the likelihood of issues like short circuits and overheating.
Telecommunications and Data Cables
For telecommunications and data transmission, insulation plays a crucial role in preserving signal quality and preventing interference.
Insulated data cables reduce signal loss and minimise electromagnetic interference (EMI), which is particularly important for high-speed data transfer in office networks, data centres, and telecommunications infrastructure.
Insulation in these applications must maintain integrity under long-term use to ensure continuous, reliable data transmission.
Specialised Environments (Marine, Medical, Aerospace)
In specialised environments like marine, medical, and aerospace, insulation must withstand extreme conditions, including high moisture, salt exposure, vibration, and temperature fluctuations.
Materials like Teflon and silicone are commonly used for their resilience in these challenging settings, providing both flexibility and robustness.
In medical and aerospace industries, insulation also needs to meet strict safety standards to ensure equipment performs reliably and safely without compromising on quality.
Benefits of High-Quality Cable Insulation
Enhanced Safety
High-quality insulation is fundamental for reducing the risk of electric shock, short circuits, and fire hazards.
In industrial and commercial settings, reliable insulation serves as a protective barrier, minimising the chance of electrical faults that can pose risks to both people and equipment.
Choosing quality insulation not only ensures regulatory compliance but also promotes a safer working and living environment.
Improved Cable Lifespan
Using durable insulation materials can significantly extend a cable’s life by protecting it from wear and environmental stress. In industrial and outdoor settings, insulation that withstands harsh conditions reduces the frequency of cable replacements and maintenance, lowering overall costs.
In both residential and commercial applications, high-quality insulation ensures that cables stay functional and safe for years, even under continuous use.
Signal Protection and Efficiency
Insulation is essential for protecting the integrity of signals, especially in data and telecommunications cables where signal quality is paramount. Quality insulation minimises signal loss, interference, and degradation, helping to maintain the efficiency and reliability of the entire system.
By reducing electromagnetic interference, well-insulated cables ensure that data is transmitted without distortion, which is crucial for accurate and high-speed communication.
This content provides a clear, professional explanation of the importance of cable insulation across various applications and the benefits of investing in high-quality materials.
Choosing the Right Cable Insulation
Factors to Consider
When selecting cable insulation, it's essential to evaluate factors such as voltage requirements, environmental exposure, temperature resistance, and mechanical demands.
Different applications call for specific insulation materials; for example, high-voltage cables require materials with excellent dielectric strength, while cables exposed to outdoor elements might need UV and moisture-resistant insulation.
Choosing the right insulation ensures not only the longevity and reliability of the cable but also the safety of the overall system.
Insulated Cable at Cableworld
At Cableworld, we offer a wide range of cables for any project. We understand that choosing the ideal cable insulation for your needs can be challenging. Our team of experts is here to guide you through the selection process, helping you assess the demands of your specific application.
By understanding your project’s unique requirements, we can recommend the best insulation materials—ensuring your cables perform efficiently and safely under all conditions.
Cable Insulation FAQs
What is cable insulation?
Cable insulation is the protective layer around the conductors within a cable, designed to prevent electrical leakage, protect against environmental factors, and ensure safety.
It’s essential for maintaining the cable’s performance and preventing accidents like short circuits and electric shock.
What materials are commonly used for cable insulation?
Common insulation materials include PVC, known for its affordability and flexibility; XLPE, valued for its high dielectric strength and thermal resistance; rubber, appreciated for flexibility and durability; and silicone, chosen for high-temperature resilience.
Each material has distinct benefits depending on the application.
What is the difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting insulation?
Thermoplastic insulation, such as PVC, becomes pliable when heated, making it suitable for general applications.
Thermosetting insulation, like XLPE, retains its shape even at high temperatures, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications that require heat resistance.
What is LSZH insulation, and where is it used?
Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) insulation emits minimal smoke and toxic fumes when exposed to fire, making it ideal for enclosed spaces and public areas where fire safety is critical, such as hospitals, airports, and office buildings.
When should I choose high-temperature insulation?
High-temperature insulation is necessary in environments where cables are exposed to intense heat, such as industrial settings, manufacturing plants, or areas with high electrical loads.
Materials like Teflon and silicone are suitable choices for high-temperature applications.
How do I select the right cable insulation for my project?
To select the right cable insulation, consider factors such as voltage, temperature range, flexibility, and environmental exposure. Consulting an expert can help match the insulation material to your specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
What are the safety benefits of quality cable insulation?
Quality insulation enhances safety by reducing the risks of electric shock, fire hazards, and short circuits. Proper insulation also protects against environmental damage, helping cables maintain their integrity and reliability over time.
Can I use PVC insulation outdoors?
While PVC is suitable for many indoor applications, it has limitations in outdoor settings where exposure to UV rays and extreme temperatures can degrade it. For outdoor use, materials with better weather resistance, such as XLPE or rubber, are typically recommended.
Alarm Cable
Arctic Grade Cable
Armoured Cable
Audio & Speaker Cable
Auto Cable
Bare Copper
Belden Equivalent Cable
Co-axial Cable
Data Cable
DC Telecom Cable
Defence Standard Cable
Emergency Lighting & Fire Detection Cable
EV Cable
Festoon
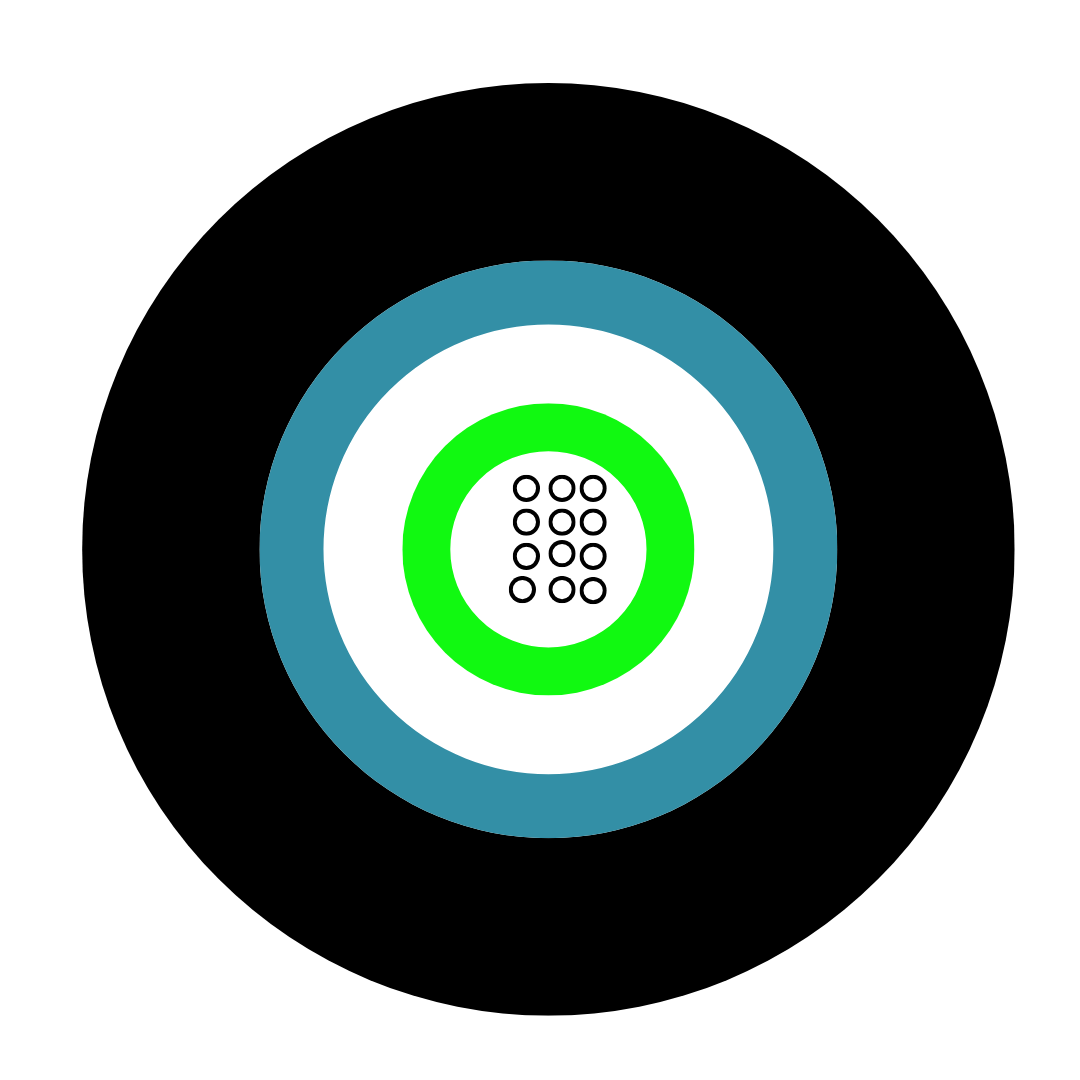
![Loose Tube Fibre Cross Section]()
Fixed Wiring PVC & LSOH Cable
Flatform
Flexible Control Cable
Flexible PVC Cable
Flexible Rubber Cable
General Wiring Cable PVC & LSOH
High Temperature Cable
High Voltage Cable
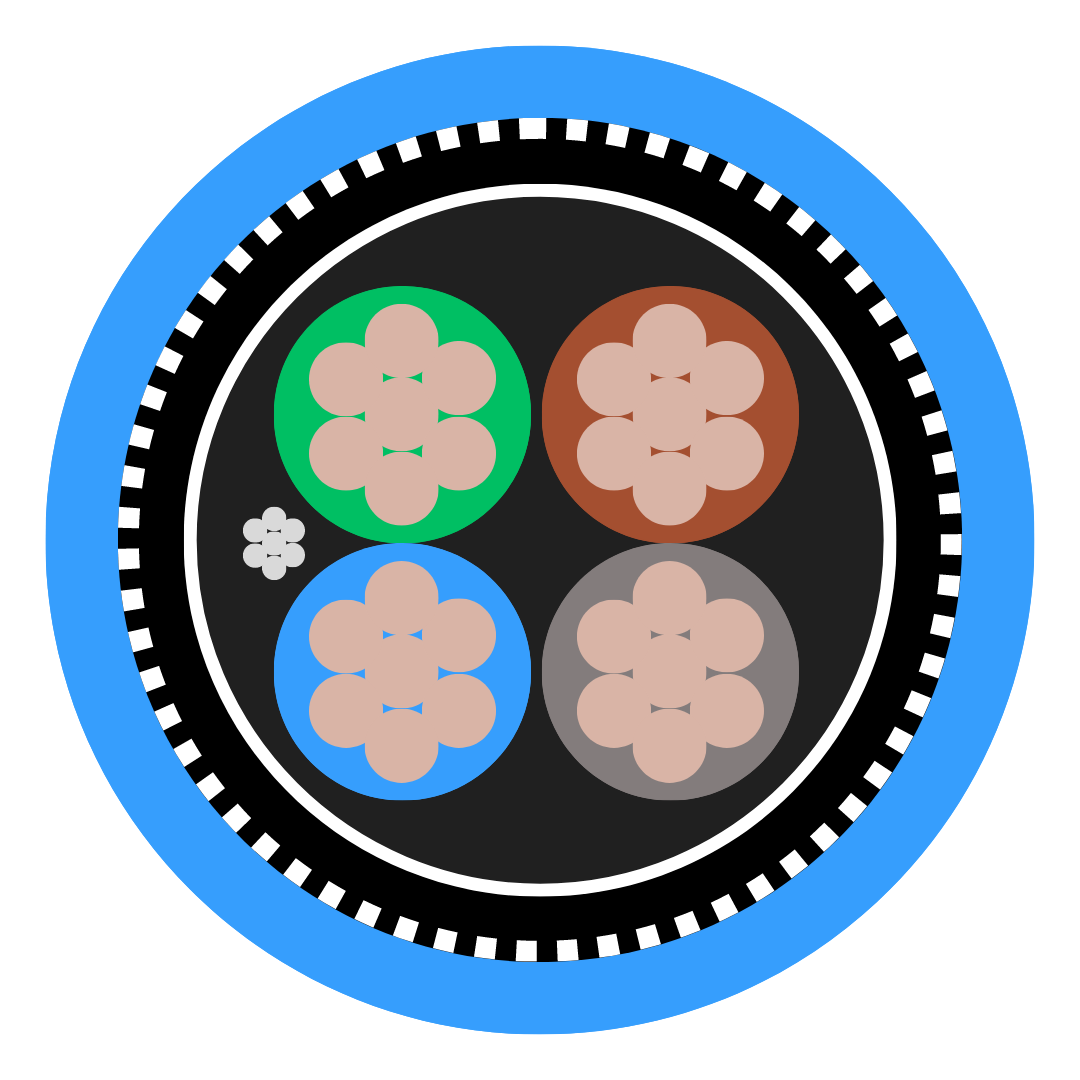
![5308 p1 t2 cat Cross Section]()
LSOH Flexible Cable
Medium Voltage Cable
NYY & N2XH Cable
Protected Wiring Cable
Silicone Cable
Solar Cable
Split Concentric Cable
Spiral Cable
Temporary Power Cable
Tri-Rated Cable
Welding Cable
Alarm Cable
Arctic Grade Cable
Armoured Cable
Audio & Speaker Cable
Auto Cable
Bare Copper
Belden Equivalent Cable
Co-axial Cable
Data Cable
DC Telecom Cable
Defence Standard Cable
Emergency Lighting & Fire Detection Cable
EV Cable
Festoon
![Loose Tube Fibre Cross Section]()
Fixed Wiring PVC & LSOH Cable
Flatform
Flexible Control Cable
Flexible PVC Cable
Flexible Rubber Cable
General Wiring Cable PVC & LSOH
High Temperature Cable
High Voltage Cable
![5308 p1 t2 cat Cross Section]()
LSOH Flexible Cable
Medium Voltage Cable
NYY & N2XH Cable
PAS - BS5308 Instrumentation Cable
Protected Wiring Cable
RS-232 Cable
RS-485 Cable
Silicone Cable
Solar Cable
Split Concentric Cable
Spiral Cable
Telephone Cable
Traffic Signal Cables
Temporary Power Cable
Tri-Rated Cable
Welding Cable
Airports
Automation & Process Control
![Automotive]()
Building & Construction
Communication & Telecommunication
Data Centres
Defence
![DNO 1]()
E-Mobility
Food & Beverage
Marine & Offshore
Mining, Drilling & Tunnelling
OEMs
Oil, Gas & Petrochemical
Rail & Metro
Renewable Energy
Switchgear
Power
Water Treatment