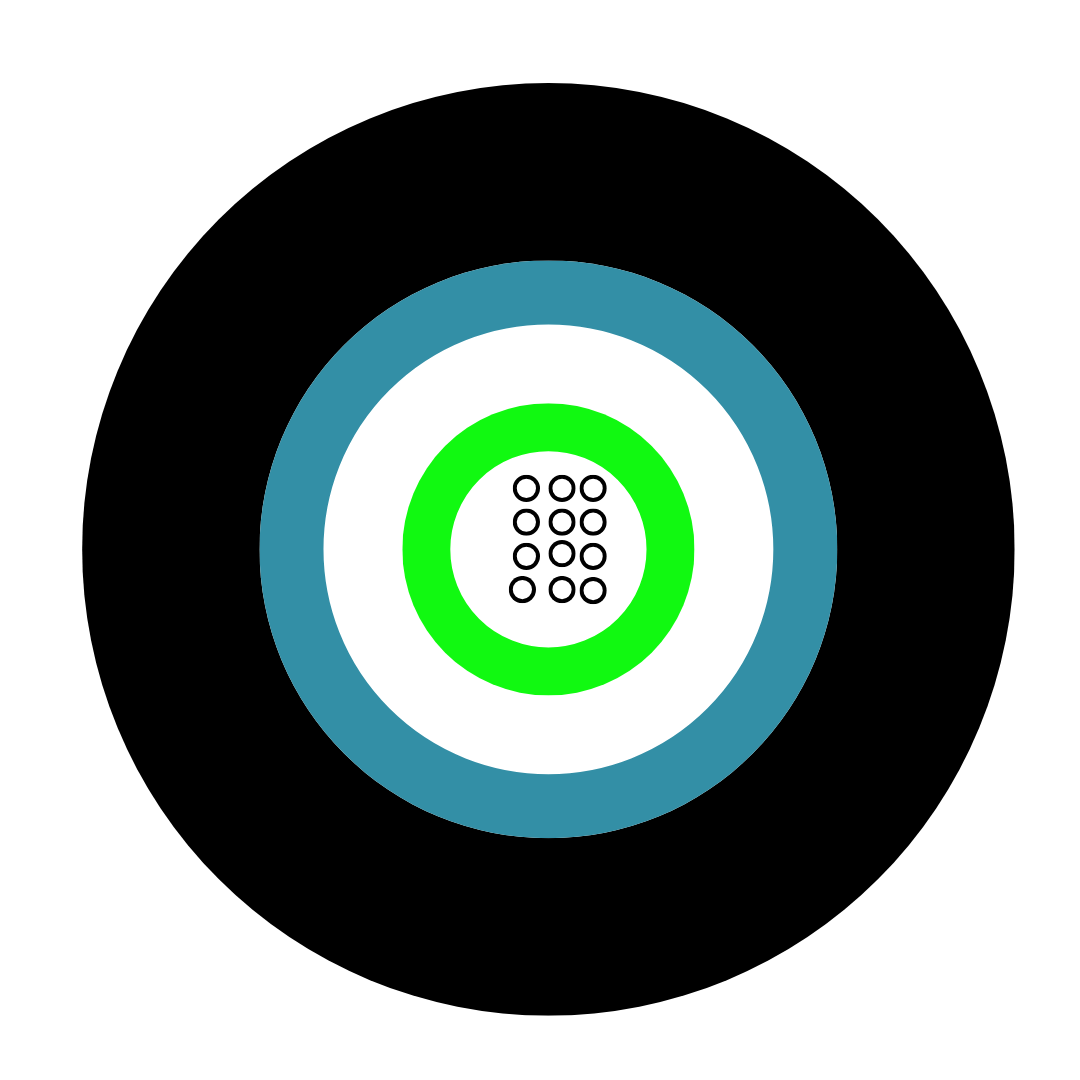
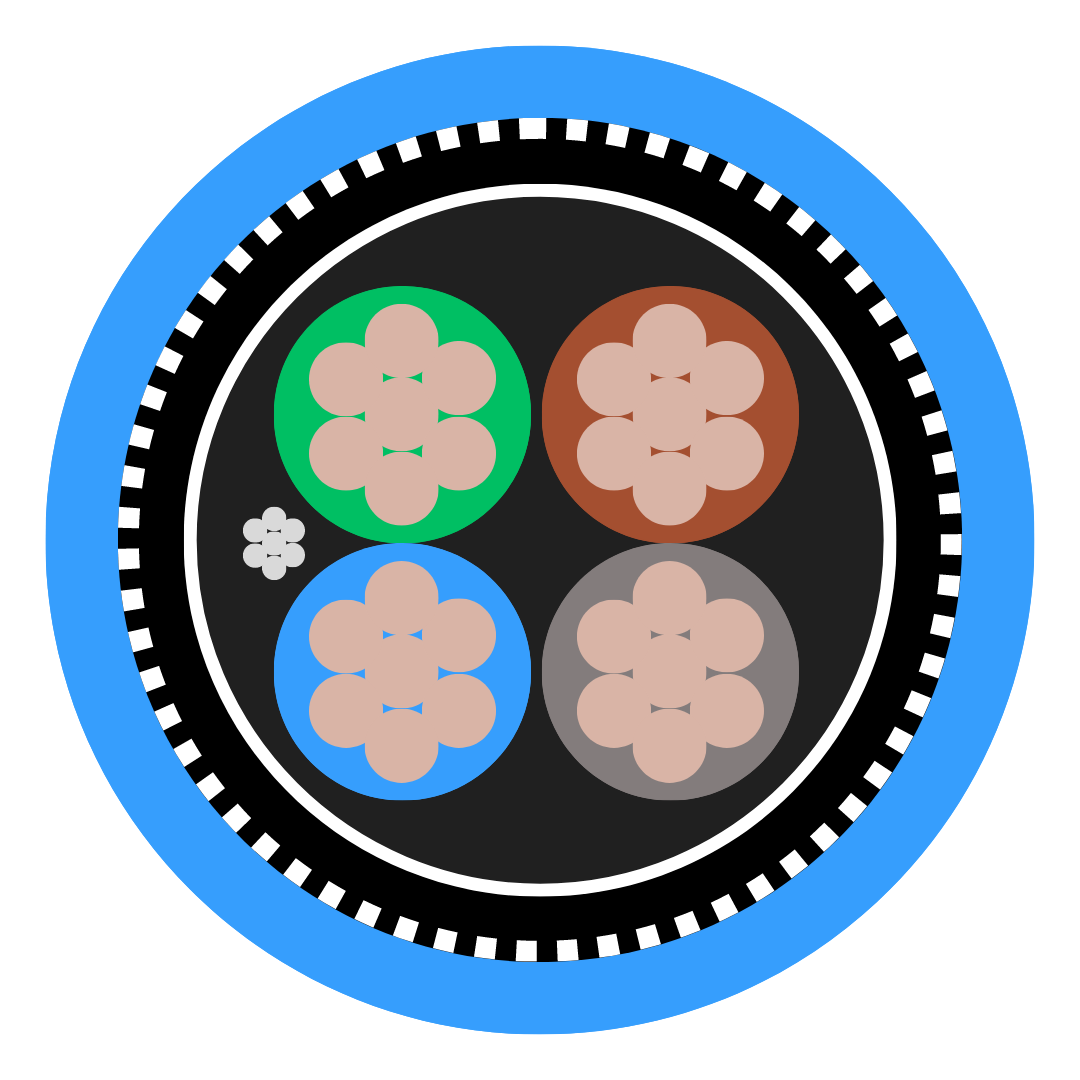
When it comes to electrical systems, selecting the right cable can make all the difference in ensuring efficiency, safety, and reliability. Two common options are single core and multi-core cables, each offering unique advantages depending on the application.
Single core cables, with their simple structure, are ideal for straightforward installations, while multi-core cables provide a more compact and versatile solution for complex systems. Understanding the differences between these two types of cables will help you make informed decisions for your projects.
At Cableworld, we specialise in supplying high-quality single and multi-core cables tailored to meet the demands of various industries across the UK. Whether you need a robust solution for industrial machinery or an efficient cable for residential use, we’re here to guide you every step of the way.
This blog will explore the key differences, applications, and benefits of single and multi-core cables, helping you choose the best option for your specific needs.
What is a Single Core Cable?
Definition and Basics
A single core cable consists of a single conductor encased in an insulating material. The conductor is typically made from copper or aluminum, chosen for their excellent electrical conductivity.
The insulation, often PVC or XLPE, provides protection against electrical leakage and external factors such as moisture and heat.
The simplicity of its structure makes single core cables a reliable option for straightforward electrical connections, offering minimal resistance and efficient performance in systems where flexibility is not a primary concern.
Applications of Single Core Cables
Single core cables are widely used in various environments due to their efficiency and ease of installation. In residential settings, they are commonly used for lighting circuits and other fixed wiring applications.
In commercial and industrial contexts, single core cables play a key role in control panels, switchboards, and other systems requiring a direct connection with minimal complexity. Their straightforward design makes them suitable for installations where the cable remains stationary.
Advantages of Single Core Cables
Single core cables offer several benefits, making them a popular choice for many installations:
Simplicity and Ease of Installation: Their straightforward design allows for quick and hassle-free installation in fixed systems.
Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to multi-core cables, single core options are often more affordable, particularly for applications requiring high volumes of cable.
Higher Current-Carrying Capacity: Single core cables can carry more current than multi-core cables of the same size, making them ideal for applications requiring high electrical loads.
With these advantages, single core cables are a trusted choice for projects requiring dependable performance and cost efficiency.
What is a Multi-Core Cable?
Definition and Basics
Multi-core cables consist of multiple insulated conductors bundled together within a single outer sheath.
Each conductor is individually insulated to ensure electrical isolation, while the outer sheath provides additional protection against external factors such as moisture, chemicals, and physical damage.
Common materials used for the conductors include copper or aluminum, chosen for their excellent conductivity. The insulation and sheathing often use materials like PVC, XLPE, or thermoplastic compounds, which offer durability and flexibility.
Some multi-core cables also feature shielding, such as braided or foil layers, to protect against electromagnetic interference (EMI), making them ideal for sensitive electronic applications.
This design enables multi-core cables to transmit multiple signals or power supplies through a single cable, reducing the need for multiple separate cables and simplifying complex systems.
Applications of Multi-Core Cables
Multi-core cables are indispensable in environments where multiple signals or power supplies are required in a compact and organised manner. Their versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications:
Control Systems: Commonly used in control panels and machinery where multiple circuits or signals need to operate in unison.
Audio-Visual Setups: Essential for connecting audio equipment, video systems, and other multimedia devices where multiple data or power lines are needed.
Industrial Machinery: Widely used in factory automation and robotics, ensuring reliable performance in systems requiring multiple electrical connections.
Whether in domestic, commercial, or industrial settings, multi-core cables simplify cable management while providing reliable performance.
Advantages of Multi-Core Cables
Multi-core cables offer several key benefits that make them a preferred choice for complex installations:
Compact Design: By bundling multiple conductors together, multi-core cables reduce clutter and save space in tight installations.
Simplified Cable Management: Using a single cable for multiple circuits reduces installation complexity and minimises the risk of tangled or misplaced wires.
Enhanced Protection: The unified outer sheath offers robust protection against environmental hazards, including moisture, UV radiation, and physical damage, ensuring long-lasting performance.
With these advantages, multi-core cables provide an efficient and reliable solution for systems requiring multiple electrical connections, particularly in demanding environments.
Key Differences Between Single Core and Multi-Core Cables
Structural Differences
Single core cables feature one conductor, typically insulated by a protective layer, making their structure simple and direct. They are designed for carrying a single current or signal, which makes them ideal for straightforward applications requiring high efficiency and minimal resistance.
In contrast, multi-core cables contain multiple individually insulated conductors housed within a single outer sheath. This allows them to carry multiple signals or power lines simultaneously, streamlining complex systems and reducing the need for multiple separate cables.
Performance Comparison
Single core cables excel in applications where high current-carrying capacity is critical. Their design minimises resistance and allows them to handle higher loads without overheating, making them ideal for power-intensive installations like switchboards or power distribution systems.
Multi-core cables, on the other hand, are built for versatility in complex setups. They can accommodate multiple circuits in one cable, simplifying installations that require multiple connections in confined spaces.
This makes them a go-to choice for control systems, automation, and audio-visual setups.
Flexibility and Durability
Multi-core cables are inherently more flexible due to their smaller individual conductors and overall design. This flexibility makes them suitable for dynamic applications, such as machinery or robotics, where the cable may need to move or bend frequently.
Single core cables, while less flexible, offer superior durability in fixed installations. Their rigid design makes them highly resistant to damage when stationary, ensuring longevity in permanent wiring systems.
Cost and Installation
Single core cables are generally more cost-effective for simple installations, especially when only one conductor is required. Their straightforward design and minimal material requirements make them an economical choice for many fixed wiring applications.
Multi-core cables, while typically more expensive upfront, can save time and reduce complexity in installations requiring multiple circuits. By bundling multiple conductors into a single cable, they streamline the setup process, reducing the need for additional cabling and simplifying cable management.
Both types of cables offer distinct advantages depending on the specific needs of your installation, making it essential to choose the right one for your application.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Single and Multi-Core Cables
Application Type
The intended application is the most crucial factor when deciding between single core and multi-core cables. Single core cables are best suited for fixed wiring systems that demand high-current capacity, such as power distribution, switchboards, and industrial machinery.
Their simplicity and efficiency make them ideal for installations where the cable remains stationary.
Multi-core cables, however, excel in dynamic systems that require multiple connections in confined spaces. These are commonly used in control systems, robotics, audio-visual setups, and other applications where space-saving and streamlined cable management are critical.
Flexibility Requirements
Flexibility is another essential consideration. Multi-core cables are inherently more flexible than single core cables due to their smaller individual conductors.
This flexibility makes them ideal for applications requiring frequent movement or bending, such as in machinery, mobile equipment, or robotics.
Single core cables, while less flexible, provide greater durability and stability in static installations.
They are an excellent choice for systems where the cable remains in place, ensuring long-term reliability without wear from movement.
Cost-Effectiveness
Evaluating the cost-to-performance ratio is important when selecting between single and multi-core cables. Single core cables are often more economical for installations requiring only one conductor, making them a cost-effective option for simple, fixed wiring systems.
Multi-core cables, though initially more expensive, can offer better value in complex installations.
By consolidating multiple conductors into a single cable, they reduce the need for additional wiring, simplify installation processes, and minimise long-term maintenance costs.
Environmental Considerations
The environment where the cable will be used plays a significant role in the selection process. Single and multi-core cables come with various insulation and sheathing options to suit different conditions:
Outdoor Applications: Choose cables with robust sheathing, such as PVC or XLPE, to resist UV exposure, moisture, and temperature fluctuations.
High-Temperature Environments: Opt for heat-resistant materials, such as silicone or Teflon, to ensure cable durability under extreme heat.
Chemical Exposure: For industrial settings with potential chemical exposure, cables with specialised insulation are essential to prevent degradation and maintain performance.
Selecting the right cable type based on these factors ensures optimal performance, safety, and longevity in your installation. At Cableworld, we provide expert guidance to help you make the best choice for your specific requirements.
UK Regulations and Standards for Single and Multi-Core Cables
Compliance with British Standards
In the UK, all electrical cables, including single and multi-core variants, must adhere to the British Standards (BS) and European Norms (EN) to ensure safety, quality, and performance. Key standards include:
BS 6004: Covers low-voltage PVC-insulated and sheathed cables.
BS EN 50525: Applies to cables used in fixed installations and includes harmonised standards for a range of insulation materials like PVC, XLPE, and LSZH.
BS 7671: The IET Wiring Regulations that provide guidelines for cable installation, including cable sizing, earthing, and safety requirements.
These standards ensure cables are manufactured and tested to meet rigorous safety and performance criteria.
Choosing cables that comply with these regulations reduces the risk of faults, improves efficiency, and ensures compatibility with UK systems.
Safety Guidelines
Using certified cables is essential for maintaining safety across residential, commercial, and industrial installations. Certified cables are rigorously tested for insulation integrity, fire resistance, and environmental durability, making them reliable for various applications.
Residential Installations: For homes, safety guidelines focus on proper cable insulation to prevent electrical shocks and fire hazards. Single core cables are often used for fixed wiring, while multi-core cables may be used for control systems or flexible connections.
Commercial Installations: In offices and retail spaces, the emphasis is on fire safety. LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) insulated cables are often recommended for environments where smoke and toxic fumes could pose risks.
Industrial Installations: For factories and large-scale operations, safety regulations mandate robust cables that can withstand high loads, mechanical stress, and exposure to harsh environments.
Adhering to these guidelines ensures compliance with legal standards like Part P of the Building Regulations and supports the overall safety of electrical systems. At Cableworld, all our single and multi-core cables meet or exceed these standards, offering you peace of mind for any project.
Single and Multi-Core Cables FAQs
What is a single core cable?
A single core cable consists of one conductor surrounded by insulation, designed for transmitting power or data. It is commonly used in fixed installations like power distribution, lighting systems, and industrial setups due to its simplicity and durability.
What is a multi-core cable?
A multi-core cable contains multiple conductors, each insulated and encased within a single outer sheath. These cables are ideal for applications requiring compact wiring solutions, such as control systems, robotics, and audio-visual setups.
What are the main differences between single core and multi-core cables?
The primary differences lie in their structure, performance, and applications. Single core cables have one conductor, making them suitable for high-current, fixed installations. Multi-core cables, with multiple insulated conductors, are more versatile and space-saving, often used in dynamic or complex systems.
Which is better: single core or multi-core?
The choice depends on the application. Single core cables are ideal for static, high-current installations, while multi-core cables are better for compact, flexible systems where multiple connections are needed.
Can I use single core cables for high-flexibility installations?
Single core cables are not suitable for applications requiring frequent movement or bending. Multi-core cables, with smaller, flexible conductors, are specifically designed for dynamic installations where flexibility is essential.
What standards do single and multi-core cables need to meet in the UK?
Both cable types must comply with relevant British Standards and European Norms, such as BS 6004 and BS EN 50525. These standards ensure safety, performance, and compatibility with UK wiring regulations like BS 7671.
Are multi-core cables more expensive than single core cables?
Multi-core cables are typically more expensive due to their complex construction and versatility. However, for installations requiring multiple connections, they can reduce overall costs by minimising the need for additional cables and simplifying the setup process.
Alarm Cable
Arctic Grade Cable
Armoured Cable
Audio & Speaker Cable
Auto Cable
Bare Copper
Belden Equivalent Cable
Co-axial Cable
Data Cable
DC Telecom Cable
Defence Standard Cable
Emergency Lighting & Fire Detection Cable
EV Cable
Festoon
![Loose Tube Fibre Cross Section]()
Fixed Wiring PVC & LSOH Cable
Flatform
Flexible Control Cable
Flexible PVC Cable
Flexible Rubber Cable
General Wiring Cable PVC & LSOH
High Temperature Cable
High Voltage Cable
![5308 p1 t2 cat Cross Section]()
LSOH Flexible Cable
Medium Voltage Cable
NYY & N2XH Cable
Protected Wiring Cable
Silicone Cable
Solar Cable
Split Concentric Cable
Spiral Cable
Temporary Power Cable
Tri-Rated Cable
Welding Cable
Alarm Cable
Arctic Grade Cable
Armoured Cable
Audio & Speaker Cable
Auto Cable
Bare Copper
Belden Equivalent Cable
Co-axial Cable
Data Cable
DC Telecom Cable
Defence Standard Cable
Emergency Lighting & Fire Detection Cable
EV Cable
Festoon
![Loose Tube Fibre Cross Section]()
Fixed Wiring PVC & LSOH Cable
Flatform
Flexible Control Cable
Flexible PVC Cable
Flexible Rubber Cable
General Wiring Cable PVC & LSOH
High Temperature Cable
High Voltage Cable
![5308 p1 t2 cat Cross Section]()
LSOH Flexible Cable
Medium Voltage Cable
NYY & N2XH Cable
PAS - BS5308 Instrumentation Cable
Protected Wiring Cable
RS-232 Cable
RS-485 Cable
Silicone Cable
Solar Cable
Split Concentric Cable
Spiral Cable
Telephone Cable
Traffic Signal Cables
Temporary Power Cable
Tri-Rated Cable
Welding Cable
Airports
Automation & Process Control
![Automotive]()
Building & Construction
Communication & Telecommunication
Data Centres
Defence
![DNO 1]()
E-Mobility
Food & Beverage
Marine & Offshore
Mining, Drilling & Tunnelling
OEMs
Oil, Gas & Petrochemical
Rail & Metro
Renewable Energy
Switchgear
Power
Water Treatment