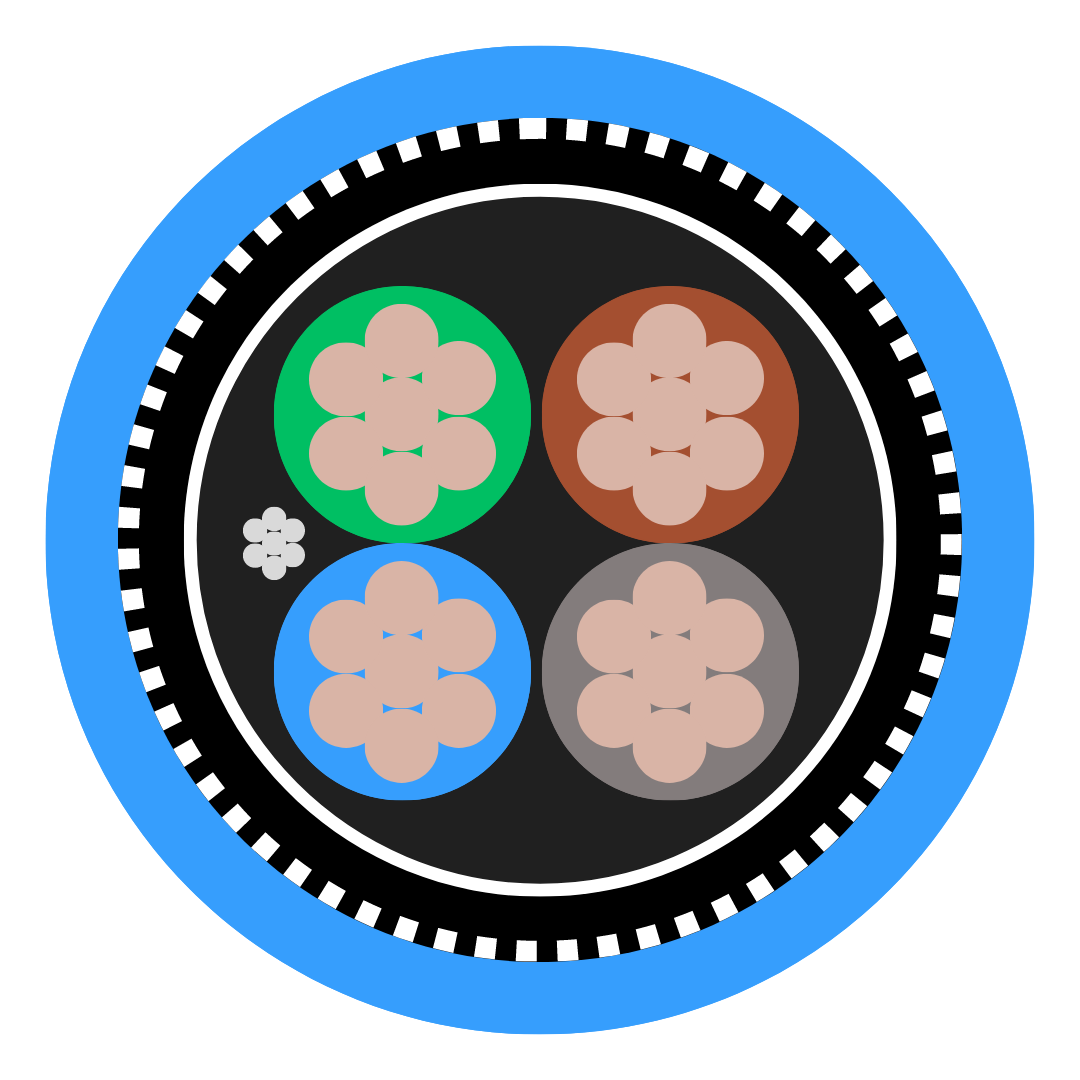
Flexible cables, often referred to as flex cables or flexible conductors, are crucial components in many electrical systems today. These cables are specifically designed to offer flexibility, durability, and resilience in environments where traditional cables may fail. Whether used in drag chain systems, audio setups, or studio broadcast systems, flexible cables ensure that electricity flows smoothly even under challenging conditions.
They are perfect for equipment and applications requiring tight bends and constant movement, such as robotic arms and conveyor systems. Their unique capability to withstand frequent bending makes them ideal for dynamic environments. Yet, it's important to know when to use them and pick the right type for the task.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of flexible cables is essential. Knowing when not to use them is just as critical to prevent any potential issues. By learning about different types of cables, individuals and organisations can make informed decisions that ensure the best performance and longevity of their electrical systems.
Key Takeaways
Flexible cables are designed for high flexibility and durability.
Ideal for moving parts and dynamic systems.
Important to choose the right type and application.
What Is a Flexible Cable?
A flexible cable, often referred to as a flex cable, is designed to bend and move frequently without breaking. Unlike regular cables, it has a small conductor diameter that allows it to be highly flexible.
These cables are often used in applications where repeated movement is required. Drag chain systems, portable appliances, and audio equipment frequently use flexible cables. Their ability to withstand bending makes them ideal for such environments.
Flexible cables are made from high-quality materials that ensure both flexibility and durability. They are commonly used in homes for connecting small appliances and in industrial settings for connecting machinery.
Flexible cables typically consist of multiple strands of wire inside an insulated jacket. This construction allows them to move easily without damage. Each component is designed to provide maximum reliability even under frequent stress.
Flex cables are categorised by their ability to handle movement. They come in different types depending on the application, including those rated for stationary, continuous movement, or even harsh outdoor conditions.
The choice to use flexible cables depends on factors like application needs and environment. Their unique properties make them a versatile solution for many electrical and mechanical challenges.
When to Use Flex Cable?
Flex cables are handy for applications where frequent movement and bending occur. They are well-suited for connecting appliances to power sources. These cables handle the movement caused by daily use without wearing out quickly.
In industrial settings, flex cables play a significant role. They can be found in machines that move or vibrate. Their durability supports tasks with repetitive motion, such as conveyors and automated arms.
Flex cables offer great utility in robotics. Robots often perform intricate and repeated movements. Using flex cables ensures long-term performance without damage. They accommodate the flexibility needed without compromising functionality.
For household wiring, flex cables connect lights and other devices. Often used in pendant lighting, they allow for easy repositioning or adjustments in style. They also remain reliable even with constant movement.
In audio and studio settings, flex cables maintain sound quality despite equipment movement. They help in the setup of systems where wiring flexibility is essential. By reducing wear and tear, they ensure consistent signal transmission.
Flex cables are essential in areas requiring flexibility and endurance. Their design allows for smooth performance under changing conditions. Whether in home use, industrial machinery, or robotics, flex cables provide resilience and adaptability necessary for reliable operation.
What Are the Advantages of Flexible Cable?
Flexible cables offer significant benefits in various applications, thanks to their ability to bend without breaking and adapt to diverse environments. Key advantages include their flexibility, versatility, and durability, making them invaluable in electrical installations and other settings.
Flexible
The flexibility of these cables is their standout feature. Designed to bend easily, flexible cables can be routed through tight spaces and around obstacles. This makes them ideal for use in environments where cables need to move or adapt frequently, such as in drag chains or robotics.
Flexible cables often consist of a multi-strand cable core wrapped in pliable cable insulation, allowing them to maintain performance without restricting movement. This flexibility also reduces the stress on the cable, which can extend its service life considerably.
Versatile
Flexible cables are incredibly versatile. They are suitable for a wide range of applications, from household electrical wiring to industrial machinery. Their ability to adapt to different shapes and spaces means they can be used in environments where traditional cables would be cumbersome.
They come in various types and sizes, tailored for specific needs, whether in data centres, automotive industries, or audio/video setups. This adaptability ensures that flexible cables meet the demands of various settings, offering a balance of performance and convenience.
Durable
Durability is another notable advantage. Despite their flexible nature, these cables are designed to withstand wear and tear, making them a reliable choice for both stationary and dynamic environments. The materials used in their cores and insulation provide resistance to mechanical stress and environmental factors.
The construction of flexible cables includes robust insulation that protects the internal wiring from damage due to pulling, bending, or external impacts. This durability extends their useful life and reduces the need for frequent replacements, offering a cost-effective solution in the long run.
Flexible Cable Types
Flexible cables are essential in many applications where movement and bending occur frequently. Here are some common types:
PVC Cables
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) cables are popular for their affordability and versatility. They offer good flexibility and are often used in light-duty applications.
Drag Chain Cables
These cables are designed to withstand continuous flexing. They are ideal for automation equipment and machinery that require constant movement.
RVV Cables
RVV cables feature soft copper conductors and PVC insulation. They are commonly used in household electrical appliances and equipment.
Flexible Armoured Cables
Flexible armoured cables provide enhanced protection with a metal layer. This makes them suitable for harsh environments where additional durability is required.
Sheathed Wires
These cables have an outer covering to protect the inner conductors from mechanical damage, moisture, and chemicals.
Flexible cables come in different materials, such as copper and aluminium. Copper is typically preferred for its excellent conductivity and flexibility. Aluminium is lighter and more cost-effective but may not support as much current as copper.
Choosing the right flexible cable depends on the specific needs of the application. Consider factors like the environment, movement type, and electrical requirements to ensure optimal performance.
When to Avoid Flexible Cable
Flexible cables, often known as flex cables, are useful in many applications. Yet, there are times when it is better to avoid them.
Fixed Wiring Systems: Using flexible cables for fixed wiring is often not recommended. Fixed systems require cables that maintain position over time, and standard flexible cables may not meet the necessary electrical codes and standards for these installations.
Flexible cables are not ideal in environments with high stress levels such as extreme temperatures. Traditional, non-flexible cables are better suited for these harsh conditions. They provide better durability and strength.
Heavy Load Applications: Avoid flexible cables for processes that involve heavy loads or high pressure. The constant pressure might cause wear and injuries to the cables over time. It may result in breakdowns that flexible cables are not designed to handle.
In settings where fire resistance is a priority, flexible cables might not always be the best choice. Some traditional cables come with specialised fire-resistant coatings that provide extra protection against environmental hazards.
Other Types of Cable
Armoured cables are used in environments where the cable needs extra protection. These cables have a layer of protective material, like steel, which shields the internal wiring from physical damage.
Coaxial cables are another type often used for transmitting television signals and internet data. They have a single copper conductor surrounded by a metal shield, which helps in preventing signal interference.
Fibre optic cables are used for high-speed data transmission over long distances. Unlike traditional metal wiring, these cables use light to transmit data. They are known for their high bandwidth and speed, making them ideal for internet and telecommunications.
PVC cables are commonly used for electrical wiring in homes and buildings. Made from polyvinyl chloride, these cables are resistant to chemicals, moisture, and abrasion.
Rubber cables are flexible and durable, often used in industrial settings where the cables may be exposed to harsh conditions. They offer good protection against wear and tear.
Silicone cables are known for their heat resistance. They perform well in high-temperature environments, making them suitable for use in appliances like ovens.
These cable types, alongside flexible cables, serve different purposes. They each offer specific features tailored to their use cases. When choosing a cable, consider the environment and the function it needs to fulfil.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a flex cable used for?
Flex cables are mainly used in applications requiring constant movement. They are vital in cable trays, portable power equipment, and renewable energy systems like wind and solar.
Can I use a 2.5 mm flex cable for sockets?
A 2.5 mm flex cable is typically suitable for socket circuits. It provides enough capacity to handle the demands of most household sockets, although it's essential always to check the specific requirements of the electrical system.
What happens if flex cable is broken?
If a flex cable is damaged or broken, it can disrupt electrical continuity and potentially become a safety hazard. It may lead to erratic performance of connected devices or pose a fire risk.
How many amps can 2.5 mm Flex carry?
A 2.5 mm flex cable can generally handle around 20 to 25 amps, depending on the conditions, including the installation environment and temperature. Always verify with local guidelines to ensure safety and compliance.
Can 1.5 mm cable take 16A?
A 1.5 mm cable can handle up to 16 amps under normal conditions. However, it's important to check manufacturer specifications and installation scenarios to avoid overloading.
What size cable do I need for 16 amps?
For a 16 amp circuit, a 1.5 mm cable is typically appropriate. It's crucial to ensure that this cable size aligns with the installation conditions and safety standards.
Can I plug 16A to 32A?
Plugging a 16A device into a 32A outlet is not recommended. This could lead to overloading the circuit and possibly damaging the equipment. Always match plugs and outlets to their respective amperage ratings.
Alarm Cable
Arctic Grade Cable
Armoured Cable
Audio & Speaker Cable
Auto Cable
Bare Copper
Belden Equivalent Cable
Co-axial Cable
Data Cable
DC Telecom Cable
Defence Standard Cable
Emergency Lighting & Fire Detection Cable
EV Cable
Festoon
Fixed Wiring PVC & LSOH Cable
Flatform
Flexible Control Cable
Flexible PVC Cable
Flexible Rubber Cable
General Wiring Cable PVC & LSOH
High Temperature Cable
High Voltage Cable
![5308 p1 t2 cat Cross Section]()
LSOH Flexible Cable
Medium Voltage Cable
NYY & N2XH Cable
Protected Wiring Cable
Silicone Cable
Solar Cable
Split Concentric Cable
Spiral Cable
Temporary Power Cable
Tri-Rated Cable
Welding Cable
Alarm Cable
Arctic Grade Cable
Armoured Cable
Audio & Speaker Cable
Auto Cable
Bare Copper
Belden Equivalent Cable
Co-axial Cable
Data Cable
DC Telecom Cable
Defence Standard Cable
Emergency Lighting & Fire Detection Cable
EV Cable
Festoon
Fibre Cable
Fixed Wiring PVC & LSOH Cable
Flatform
Flexible Control Cable
Flexible PVC Cable
Flexible Rubber Cable
General Wiring Cable PVC & LSOH
High Temperature Cable
High Voltage Cable
![5308 p1 t2 cat Cross Section]()
LSOH Flexible Cable
Medium Voltage Cable
NYY & N2XH Cable
PAS - BS5308 Instrumentation Cable
Protected Wiring Cable
RS-232 Cable
RS-485 Cable
Silicone Cable
Solar Cable
Split Concentric Cable
Spiral Cable
Telephone Cable
Temporary Power Cable
Traffic Signal Cables
Tri-Rated Cable
Welding Cable