Fibre optics are a critical component in modern networking, offering high-speed data transmission over long distances. At Cableworld, we understand the importance of choosing the right type of fibre for your needs.
That’s why in this guide, we’ll be explaining the differences between multimode and single mode fibre, their applications, and their advantages.
What is Fibre Optic Cable?
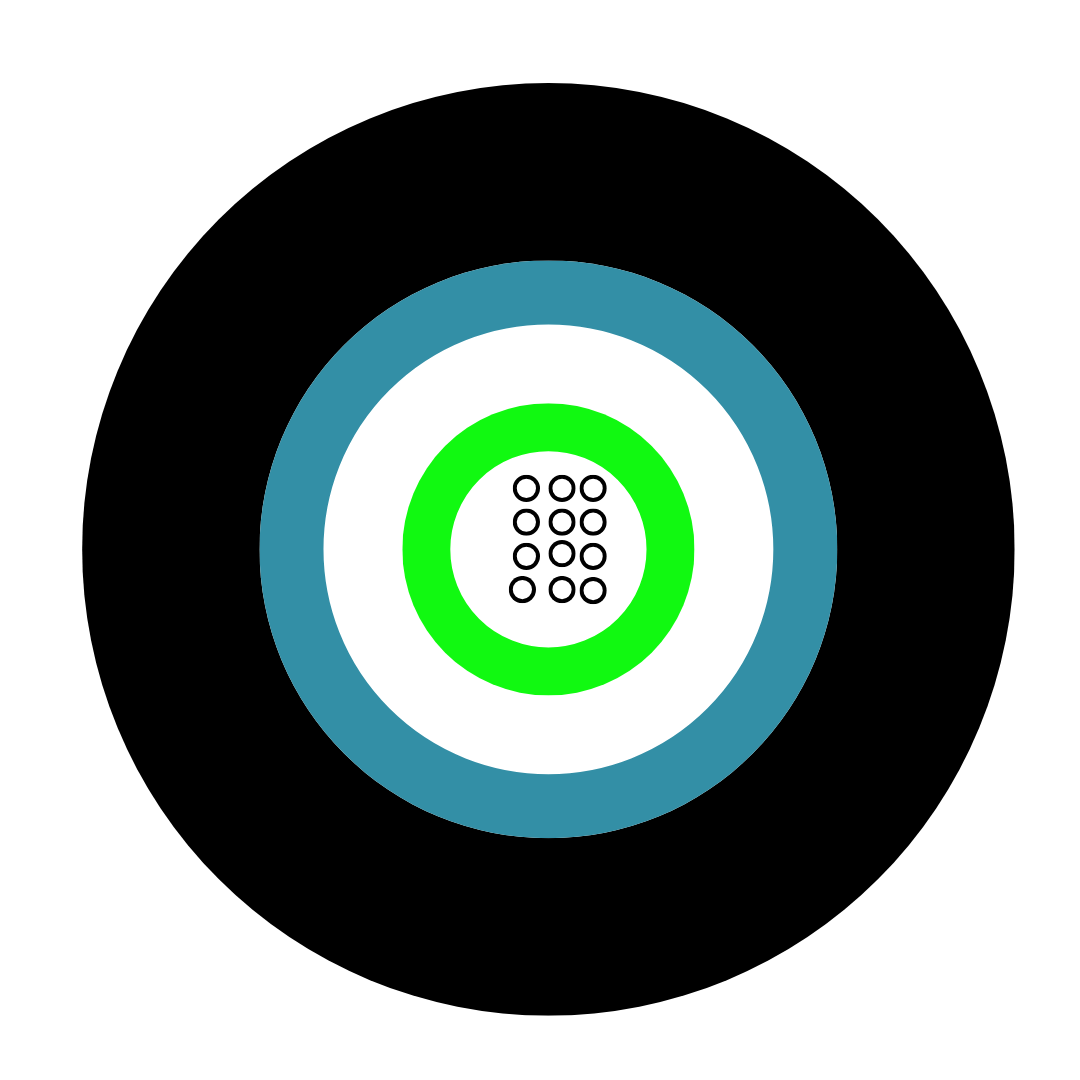
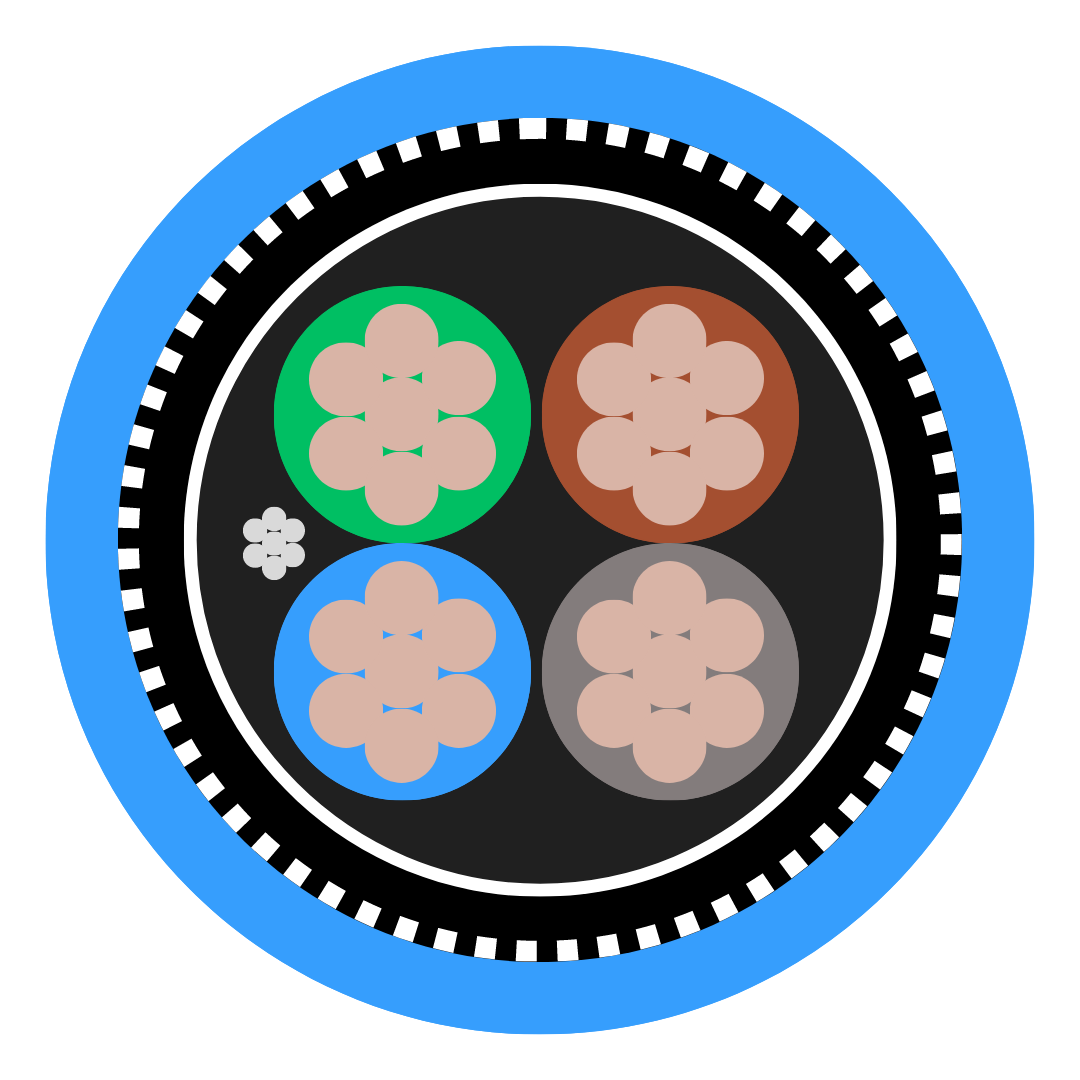
Fibre optic cables are a type of network cable that uses light to transmit data. These cables contain strands of glass fibres inside an insulated casing, which carry data signals in the form of light. This technology allows for faster data transmission over greater distances compared to traditional copper cables.
The basic components of a fibre optic cable include the core, cladding, buffer coating, and jacket, each playing a crucial role in protecting the fibres and ensuring efficient data transmission.
What is Single Mode Fibre?
Single mode fibre optic cable is designed to carry light directly down the fibre, allowing for a single light path. This type of cable has a very thin core, typically around 8-10 micrometres in diameter, which allows the transmission of data over long distances with minimal signal loss.
Key Characteristics
The core diameter is about 8-10 micrometres, which is smaller than that of multimode fibre.
It uses a single light mode to transmit data, reducing attenuation and interference.
Single mode fibre is ideal for long-distance telecommunications and high-speed data transfer, offering higher bandwidth capabilities compared to multimode fibre.
Applications of Single Mode Fibre
Single mode fibre is commonly used in long-distance telecommunications, data centres, and high-speed networks. Its ability to transmit data over longer distances with less signal loss makes it ideal for cases that require robust and efficient data transfer.
What is Multimode Fibre?
Multimode fibre optic cable is designed to carry multiple light modes simultaneously. It has a larger core diameter, typically around 50-62.5 micrometres, which allows multiple light paths to travel down the fibre. This makes it suitable for shorter distances and high-bandwidth applications.
Key Characteristics
The core diameter ranges from 50 to 62.5 micrometres, which is larger than single mode fibre.
It allows multiple light modes to propagate, which can lead to higher dispersion and attenuation.
Multimode fibre is ideal for shorter distance data communication and is commonly used in local area networks (LANs).
Applications of Multimode Fibre
Multimode fibre is frequently used in local area networks (LANs), short-distance data communication, and other scenarios where high bandwidth over shorter distances is required. Its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation make it a popular choice for these applications.
What’s the Difference Between Single Mode and Multimode Fibre?
Core Diameter
The core diameter is a primary difference between single mode and multimode fibres. Single mode fibres have a core diameter of 8-10 micrometres, while multimode fibres have a larger core diameter of 50-62.5 micrometres.
This difference affects how light propagates through the fibres and their respective performance characteristics.
Light Propagation
In single mode fibre, light travels straight down the fibre with minimal dispersion, allowing for longer distances and higher bandwidths. Multimode fibre allows multiple light paths, which can lead to greater dispersion and attenuation, making it suitable for shorter distances.
Bandwidth and Distance
Single mode fibre offers higher bandwidth and can transmit data over longer distances without significant signal loss, making it ideal for long-haul and high-speed applications. Multimode fibre, while providing high bandwidth for short distances, is not suitable for long-distance applications due to higher dispersion and attenuation rates.
Choosing Between Single Mode and Multimode Fibre
When deciding between single mode and multimode fibre optic cables, several key factors should be taken into account.
Distance Requirements
Single mode fibre is ideal for long-distance transmission due to its low attenuation and high bandwidth capabilities. If your application involves transmitting data over extensive distances, single mode fibre is the preferable choice. On the other hand, multimode fibre is more suited for short-distance applications, typically within a few hundred metres, such as in local area networks (LANs).
Budget Constraints
Cost is a significant factor in choosing between single mode and multimode fibre. Multimode fibre cables and their associated components, such as transceivers, tend to be less expensive than single mode solutions.
Therefore, for budget-sensitive projects where the distance and bandwidth requirements are within the capabilities of multimode fibre, it is a cost-effective option.
Bandwidth Needs
The bandwidth requirements of your application are also crucial. Single mode fibre supports higher bandwidths and is therefore suitable for high-speed data transmission over long distances. If your application demands high data rates over long distances, single mode fibre is the best choice.
Multimode fibre, while also supporting high data rates, is typically used for shorter distances and can be a practical choice for applications like data centres and LANs where the distances are not as extensive.
Whether you need single mode for long-distance communication or multimode for short-range, high-bandwidth applications, Cableworld provides a comprehensive range of fibre optic cables to meet your requirements.
Single Mode vs Multi Mode Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between single mode and multimode fibre?
Single mode fibre has a smaller core diameter (8-10 micrometres) and supports long-distance transmission with higher bandwidth capabilities due to minimal dispersion and attenuation. Multimode fibre has a larger core diameter (50-62.5 micrometres) and is suitable for short-distance applications with high data rates but higher dispersion and attenuation.
Which is better for long-distance transmission, single mode or multimode fibre?
Single mode fibre is better for long-distance transmission. It can transmit data over several kilometres with minimal signal loss, making it ideal for telecommunications and long-haul data transfer.
Can single mode and multimode fibres be used together?
In general, single mode and multimode fibres are not used together within the same network due to differences in core diameters and light propagation methods. However, with the use of media converters, it is possible to interconnect networks using both types of fibre.
What are the cost differences between single mode and multimode fibre?
Multimode fibre solutions are generally less expensive than single mode fibre solutions. This includes the cost of the fibre cables themselves and associated components like transceivers and connectors.
How do I determine the right type of fibre optic cable for my project?
To determine the right type of fibre optic cable, consider the distance over which you need to transmit data, your budget, and the bandwidth requirements of your application. Consulting with a network design professional or using a cable selection tool can help you make an informed decision.
What are the typical applications for multimode fibre?
Multimode fibre is typically used in local area networks (LANs), data centres, and other short-distance communication applications where high bandwidth over shorter distances is required.
What are the typical applications for single mode fibre?
Single mode fibre is used in long-distance telecommunications, high-speed data centres, metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs) where high bandwidth and long-distance transmission are critical.
Is single mode fibre more difficult to install than multimode fibre?
The installation process for single mode fibre can be more challenging due to its smaller core diameter, which requires precise alignment and splicing techniques. However, with proper tools and training, both single mode and multimode fibres can be installed effectively.
Alarm Cable
Arctic Grade Cable
Armoured Cable
Audio & Speaker Cable
Auto Cable
Bare Copper
Belden Equivalent Cable
Co-axial Cable
Data Cable
DC Telecom Cable
Defence Standard Cable
Emergency Lighting & Fire Detection Cable
EV Cable
Festoon
![Loose Tube Fibre Cross Section]()
Fixed Wiring PVC & LSOH Cable
Flatform
Flexible Control Cable
Flexible PVC Cable
Flexible Rubber Cable
General Wiring Cable PVC & LSOH
High Temperature Cable
High Voltage Cable
![5308 p1 t2 cat Cross Section]()
LSOH Flexible Cable
Medium Voltage Cable
NYY & N2XH Cable
Protected Wiring Cable
Silicone Cable
Solar Cable
Split Concentric Cable
Spiral Cable
Temporary Power Cable
Tri-Rated Cable
Welding Cable
Alarm Cable
Arctic Grade Cable
Armoured Cable
Audio & Speaker Cable
Auto Cable
Bare Copper
Belden Equivalent Cable
Co-axial Cable
Data Cable
DC Telecom Cable
Defence Standard Cable
Emergency Lighting & Fire Detection Cable
EV Cable
Festoon
![Loose Tube Fibre Cross Section]()
Fixed Wiring PVC & LSOH Cable
Flatform
Flexible Control Cable
Flexible PVC Cable
Flexible Rubber Cable
General Wiring Cable PVC & LSOH
High Temperature Cable
High Voltage Cable
![5308 p1 t2 cat Cross Section]()
LSOH Flexible Cable
Medium Voltage Cable
NYY & N2XH Cable
PAS - BS5308 Instrumentation Cable
Protected Wiring Cable
RS-232 Cable
RS-485 Cable
Silicone Cable
Solar Cable
Split Concentric Cable
Spiral Cable
Telephone Cable
Traffic Signal Cables
Temporary Power Cable
Tri-Rated Cable
Welding Cable
Airports
Automation & Process Control
![Automotive]()
Building & Construction
Communication & Telecommunication
Data Centres
Defence
![DNO 1]()
E-Mobility
Food & Beverage
Marine & Offshore
Mining, Drilling & Tunnelling
OEMs
Oil, Gas & Petrochemical
Rail & Metro
Renewable Energy
Switchgear
Power
Water Treatment