Fibre optic cable is a type of advanced network cable. Compared to traditional metal conductor alternatives, fibre optic offers significantly better performance when it comes to bandwidth and data carrying. In this complete guide we’ll be explaining all you need to know about fibre optic cable.
What is Optical Fibre?
Fibre optic technology is a cable-based communication system that is highly popular thanks to its reliability and versatility, making it suitable for a wide range of applications and industries.
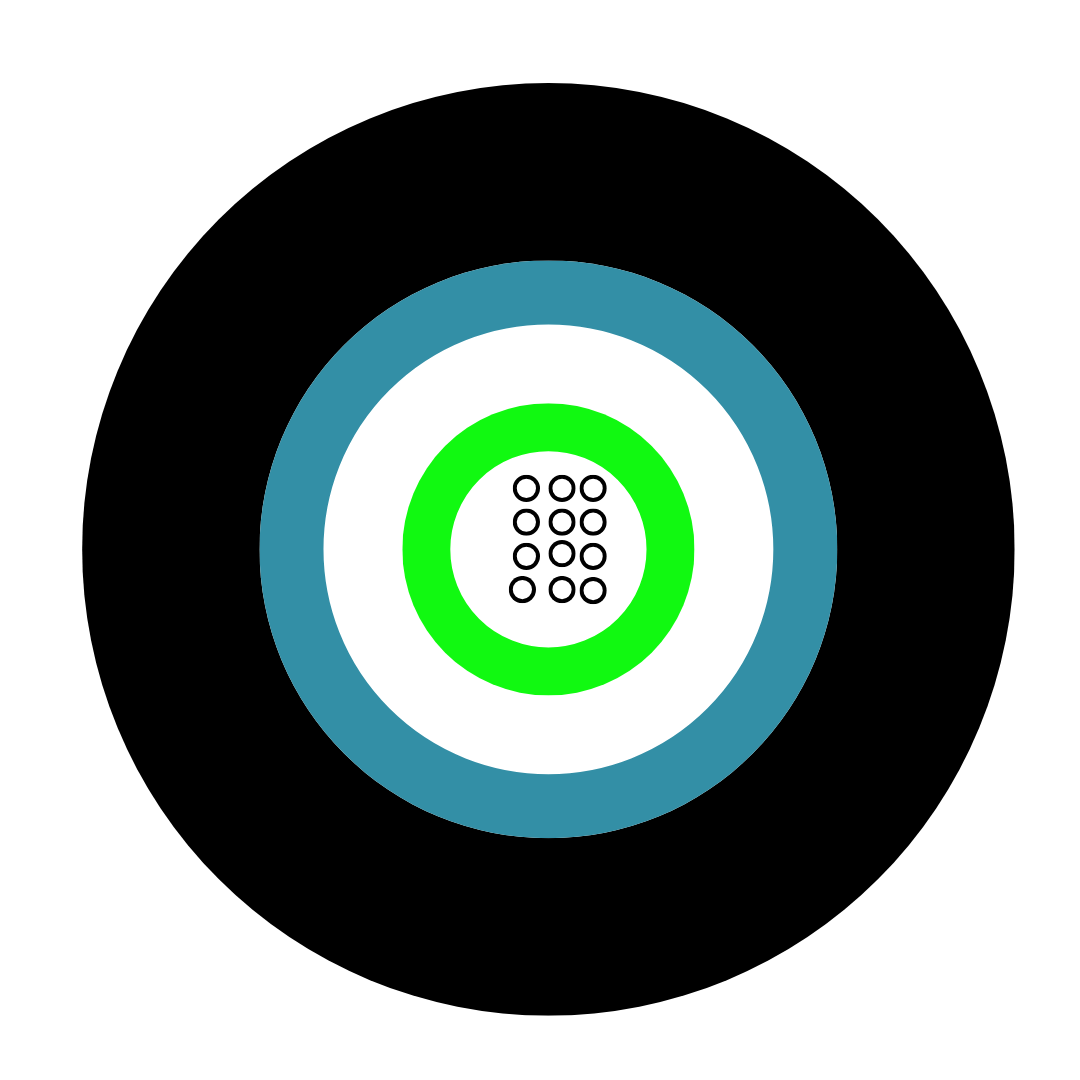
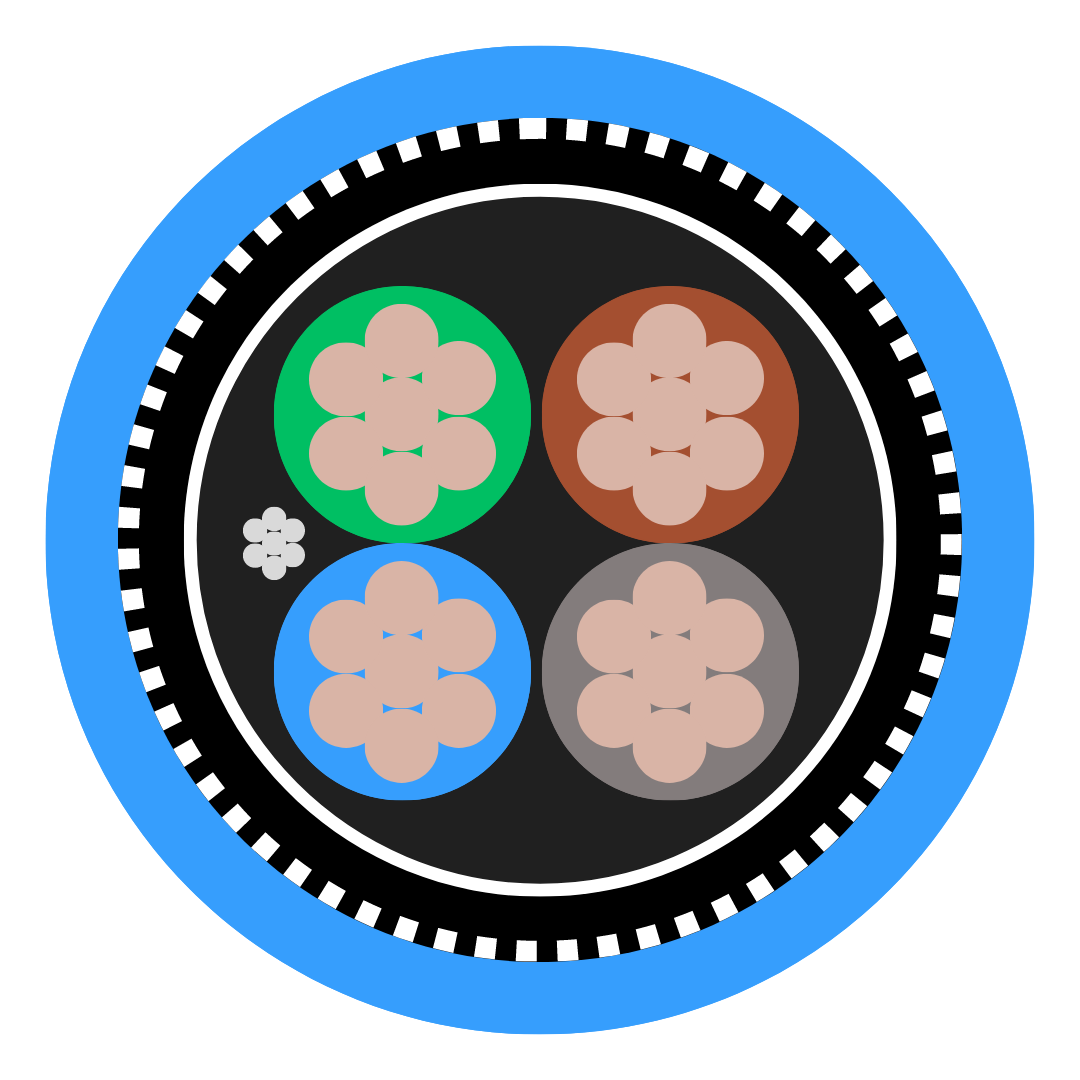
Optical fibre cable is used to transfer information via light pulses, which travel along one or more transparent plastic or glass cores. Sometimes, this can be over several hundred cores, each of which is slightly wider than a hair and typically surrounded by plastic or glass cladding.
Around this is a sheath made from layers of insulated casing, as well as a final outer jacket to protect the entire cable.
Uses of Optical Fibre Cable
Fibre optic cables are used across a variety of applications such as internet and broadband, phone lines, networking and telecommunications. It can also be used for lighting and interior decor in homes and workplaces.
One of the key benefits of fibre optic cable is its space saving ability as it isn’t as bulky as traditional cabling. This also makes it popular for safety and lighting features in vehicles, where very little space is available and medical applications, where the monitoring of electric currents, sounds and chemicals is required.
Fibre Optic Cable for Internet and Networking
Fibre optic cable offers higher speeds and bandwidth than standard ethernet or Wi-Fi signals delivered by coaxial or copper wire. This makes it a popular internet cable option in many homes across the UK, particularly as more of us require fast speeds for streaming.
Fibre Optic Cable for Lighting
Optical fibre technology is commonly used for LED lighting in domestic and commercial properties thanks to its ability to transmit data across a wide range of colours and patterns.
Another benefit of fibre optic cables is their high efficiency, as they don’t use as much electricity compared to a standard bulb. This is an important consideration for homeowners and businesses looking to become more environmentally friendly.
Fibre Cable Specification
Fibre Optic Cable Transmission Speed
The transfer rates of fibre optic data transfer is dependent on a number of aspects– primarily the cable mode. Optical fibres can be either single-mode or multi-mode. Single-mode fibre cable is suitable for long-distance data transmission, while multi-mode fibre cable is ideal for shorter distances and higher bandwidth requirements.
Fibre Optic Cable Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the maximum amount of data transmitted over a connection in a given amount of time. More specifically, it is the frequency where the magnitude of the response has decreased to half its zero frequency value.
As fibre optic cables can transmit data quickly, bandwidth is high.
Benefits of Fibre Optic Cable
There are a number of reasons to choose fibre optic cable over traditional copper conductor cables.
Speed
Fibre optic cables have a great speed advantage as they use light pulses to convey information. This outdoes even high-grade copper cables such as Cat5 and Cat6.
Distance
Thanks to their low signal power loss rate, fibre optic cables can carry signals over much longer distances than other types of cable. With an ideal network setup, some fibre optics can carry signals over hundreds of kilometres, whereas standard copper cables are limited to 328 feet for decent quality transfer.
Less Interference
Fibre optic doesn’t carry physical electrical signals, meaning they’re much better protected against interference and cross-talk than metal cables.
Safety
While fibre optic cables are lighter and thinner than standard copper cables, they’re actually a lot sturdier. This means they’re able to withstand much greater forces and are less likely to become damaged. It’s also worth noting that you never have to worry about fibre optic becoming a fire hazard, as glass fibres don’t carry any current.
Fibre Optic Cable FAQs
When should single-mode fibre be used in an AV system?
Single-mode fibre is ideal for long transmissions of up to 30km. It’s optimal for transmitting signals between buildings across a single site or university campus for example.
When should multi-mode fibre be used in an AV system?
Multi-mode fibre is used for transmitting signals across hundreds of metres. It’s the perfect solution for transmitting signals between the floors of a building or from one room to another.
What’s the difference between single-mode fibre and multi-mode fibre?
The key difference is the core. Single-mode fibre has a step index core, while multi-mode has a graded index core.
How far can optical fibres be bent during installation?
The minimum bend radius can differ per manufacturer. It’s important not to bend the optical fibre beyond the recommendation as this can cause loss in the fibre optic signal and damage the fibre. If you cannot find the manufacturer’s minimum bend radius, the rule of thumb is that the minimum bend radius is 20 times the cable diameter for standard fibre optic cable.
Alarm Cable
Arctic Grade Cable
Armoured Cable
Audio & Speaker Cable
Auto Cable
Bare Copper
Belden Equivalent Cable
Co-axial Cable
Data Cable
DC Telecom Cable
Defence Standard Cable
Emergency Lighting & Fire Detection Cable
EV Cable
Festoon
![Loose Tube Fibre Cross Section]()
Fixed Wiring PVC & LSOH Cable
Flatform
Flexible Control Cable
Flexible PVC Cable
Flexible Rubber Cable
General Wiring Cable PVC & LSOH
High Temperature Cable
High Voltage Cable
![5308 p1 t2 cat Cross Section]()
LSOH Flexible Cable
Medium Voltage Cable
NYY & N2XH Cable
Protected Wiring Cable
Silicone Cable
Solar Cable
Split Concentric Cable
Spiral Cable
Temporary Power Cable
Tri-Rated Cable
Welding Cable
Alarm Cable
Arctic Grade Cable
Armoured Cable
Audio & Speaker Cable
Auto Cable
Bare Copper
Belden Equivalent Cable
Co-axial Cable
Data Cable
DC Telecom Cable
Defence Standard Cable
Emergency Lighting & Fire Detection Cable
EV Cable
Festoon
![Loose Tube Fibre Cross Section]()
Fixed Wiring PVC & LSOH Cable
Flatform
Flexible Control Cable
Flexible PVC Cable
Flexible Rubber Cable
General Wiring Cable PVC & LSOH
High Temperature Cable
High Voltage Cable
![5308 p1 t2 cat Cross Section]()
LSOH Flexible Cable
Medium Voltage Cable
NYY & N2XH Cable
PAS - BS5308 Instrumentation Cable
Protected Wiring Cable
RS-232 Cable
RS-485 Cable
Silicone Cable
Solar Cable
Split Concentric Cable
Spiral Cable
Telephone Cable
Traffic Signal Cables
Temporary Power Cable
Tri-Rated Cable
Welding Cable
Airports
Automation & Process Control
![Automotive]()
Building & Construction
Communication & Telecommunication
Data Centres
Defence
![DNO 1]()
E-Mobility
Food & Beverage
Marine & Offshore
Mining, Drilling & Tunnelling
OEMs
Oil, Gas & Petrochemical
Rail & Metro
Renewable Energy
Switchgear
Power
Water Treatment